

Right Click, select properties and on the Details tab select Hardware Ids. Just find your AHCI controller under IDE ATA/ATAPI controllers: If you have another machine with the same SATA controller which is already in AHCI mode then you can simply look up the values in Device Manager. Unfortunately both the Hardware Id and Device Instance Path differ for each SATA controller. On a Dell Precision M4500 the reg file to accomplish these steps looks like this: Add the Device Instance Path of your SATA controller to the iaStor registry key.
#Change ahci to raid windows 10 registry drivers
Add Intel’s iaStor driver to both registry and drivers folder.
 Add the Hardware (PnP) Id of your SATA controller to the Critical Device Database in the registry. Set the Microsoft MSAHCI driver to Autostart. However for Intel SATA Controllers (the most common) we need to perform a few additional steps.Īfter some experiments I was able to create a recipe for it: There is a Microsoft KB Article that describes the steps required to fix this problem. On my Dell laptop, the setting is System Configuration | SATA Operation:īut if we change this setting after we have installed the Operating System it will crash on boot with a STOP 0x0000007B INACCESSABLE_BOOT_DEVICE error: The switch itself is very easy, just go to your bios and change the setting. So the question is: how do we switch the SATA Operation Mode from ATA or IRRT to AHCI?
Add the Hardware (PnP) Id of your SATA controller to the Critical Device Database in the registry. Set the Microsoft MSAHCI driver to Autostart. However for Intel SATA Controllers (the most common) we need to perform a few additional steps.Īfter some experiments I was able to create a recipe for it: There is a Microsoft KB Article that describes the steps required to fix this problem. On my Dell laptop, the setting is System Configuration | SATA Operation:īut if we change this setting after we have installed the Operating System it will crash on boot with a STOP 0x0000007B INACCESSABLE_BOOT_DEVICE error: The switch itself is very easy, just go to your bios and change the setting. So the question is: how do we switch the SATA Operation Mode from ATA or IRRT to AHCI? 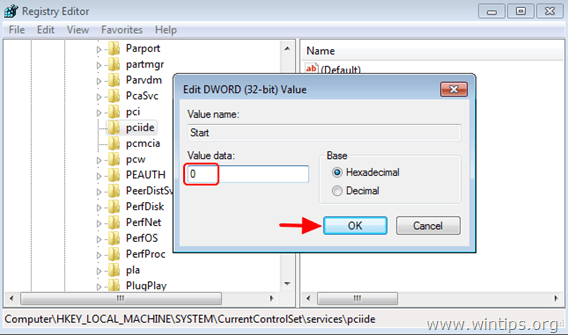
Please note that the IRRT (integrated raid) mode is supposed to support all functionality of AHCI but in my experience it doesn’t.
AHCI is required for self encrypting hard drives. AHCI is a requirement for the TRIM command. AHCI has a higher performance than ATA. Many vendors set the SATA Operation Mode to ATA by default because it’s the most compatible mode but there are a few reasons why you might want to change it: The AHCI mode offers extra features such as hot swapping and native command queuing. Modern systems usually offer different SATA Operation Modes such as ATA, AHCI or IRRT.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
